|
Omega Chess is played with two players. As in Standard Chess, before the
start of the game, the players must decide which color pieces they will play,
white or black. Just like chess, white makes the first move followed by
black. All the familiar pieces in Omega Chess follow the
same rules as in Traditional Chess, except for pawns which have been modified
for play on a 10x10 board.Omega Chess is played with the same rules as chess, except for the Pawns.
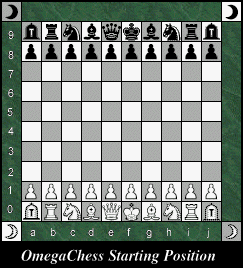 Setting up the Omega Chess
board. The Omega Chess board has 104 squares with a 10 x 10 square
playing field and four Wizard squares at each corner. It is important to
realize that in the course of the game these Wizard squares are part of the
board and can be occupied by any piece (except for pawns and rooks,
which have no way of getting there). Setting up the Omega Chess
board. The Omega Chess board has 104 squares with a 10 x 10 square
playing field and four Wizard squares at each corner. It is important to
realize that in the course of the game these Wizard squares are part of the
board and can be occupied by any piece (except for pawns and rooks,
which have no way of getting there).
Following the diagram, position the board so that a dark
corner square is on the right-hand side of each player. Each of the player's Wizards are placed on the diagonal corner
squares that extend beyond the 10 x 10 playing field. Next place the
Champions on the corner squares of the 10 x 10 playing field, followed by the
Rooks, Knights and Bishops. Then the Queen is placed on the square matching
her own colour and the King is placed beside the Queen. One Pawn is placed
on the row of squares in front of each piece excluding the Wizard.
Note: For notation purposes, the ranks and files are
as indicated in the diagram above and the squares for the Wizards are
designated w1 to w4, beginning at White's Queen Wizard's square and
proceeding counter-clockwise.
|
|
|
The Object of the Game
The object of the game remains the same as in Standard Chess; to
checkmate the opposing King. When a King is directly threatened by an
opponent's piece, the King is in check. The player in
check must respond in one of three ways. He must either;
- Capture the threatening piece
- Block the path of the threatening piece or,
- Move the King to an unthreatened square
Checkmate occurs when a player's King is in check and the player has no
way to get out of check on the next move. This ends the game with the
capturing player as the clear winner.
A game of chess can also end in a draw in which there is no clear winner. A draw
may occur one of four ways:
- Stalemate: A stalemate occurs if a player who is not in check
cannot move any piece, including the King, without placing their
King in check.
- Insufficient Mating Material: When neither player has the pieces
needed to checkmate the other player. eg. Bishop and King vs. King.
- Threefold Repetition of Position: The game is drawn if the
same position (with the same person on move) has appeared on
the chessboard three times.
- 50 Moves Rule: If there have been 50 consecutive moves of White
and Black without any piece capture or any pawn move.
If a player feels that their position is hopeless, the player may end
the game by conceding to the other player. Alternatively, if the players feel
that neither side can win, they may agree to a draw.
|
|
|
How The Pieces Move and Capture
All Chess pieces (including the Omega Chess pieces) capture an opponent's
piece by landing on the square occupied by the opponent's piece.
The King, Queen, Bishop, Knight and Rook move and capture in the
same way as Standard Chess. Virtually nothing about chess has changed with
Omega Chess.
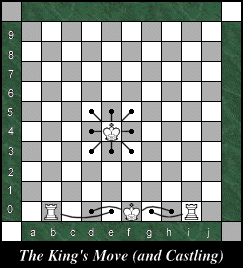 The King
can move one square in any direction, except when castling.
Castling is a defensive move using the King and
either Rook. A player can castle provided that: The King
can move one square in any direction, except when castling.
Castling is a defensive move using the King and
either Rook. A player can castle provided that:
- The King is not in check.
- The King and the castling Rook have not been moved during the game.
- All the squares between the King and the castling Rook are unoccuppied.
- The King would not be moving through or landing on a square under threat.
When castling, the King either moves two squares towards the King's Rook,
or the King move two squares towards the Queen's Rook. The King's Rook or
Queen's Rook then moves to the square the King moved through.
|
|
|
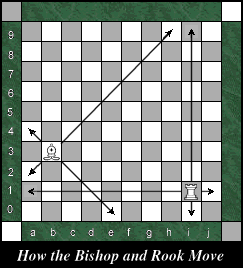 The Bishop
is a line piece which moves in an unobstructed path any number of
squares diagonally. As can be seen in the diagram, a Bishop only occupies
squares of its starting color. The Bishop
is a line piece which moves in an unobstructed path any number of
squares diagonally. As can be seen in the diagram, a Bishop only occupies
squares of its starting color.
The Rook is also a line piece. It moves in an
unobstructed path any number of squares orthogonally (horizontally or
vertically).
|
|
|
|
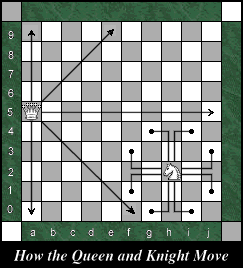 The Queen
is the most powerful chess piece, combining the powers of the Bishop
and the Rook. It moves along an unobstructed path any number of squares
diagonally or orthogonally. The Queen
is the most powerful chess piece, combining the powers of the Bishop
and the Rook. It moves along an unobstructed path any number of squares
diagonally or orthogonally.
The Knight is a leaper. Unlike a line piece it
doesn't require an unobstructed path to move along and it can jump over
other pieces. The Knight can move two squares horizontally or vertically
and then one square to either side. Refer to the diagram for a clearer
illustration of the Knight's move.
|
|
|
How The Omega Chess Pieces Move

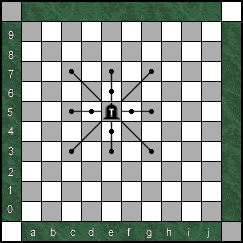 The Champion,
like the Knight, is classified as a leaper. It can move one
square orthogonally, forward, backward or to either side. Or the Champion
can jump two squares forward or backward or to either side, or jump two
squares diagonally in all four directions. The Champion can jump over pieces
and it can control up to twelve squares. (See diagram).The
Champion cannot move one square diagonally. The Champion,
like the Knight, is classified as a leaper. It can move one
square orthogonally, forward, backward or to either side. Or the Champion
can jump two squares forward or backward or to either side, or jump two
squares diagonally in all four directions. The Champion can jump over pieces
and it can control up to twelve squares. (See diagram).The
Champion cannot move one square diagonally.
From the opening position, the Champion can immediately enter a game by jumping to squares a2 - c2, h2 - j2, j7 - h7, a7 - c7.
|
|
|
|

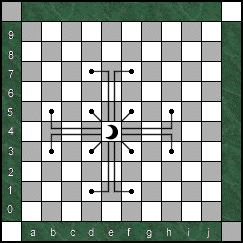 The Wizard
is also classified as a leaper. It can move one square
diagonally in all four directions. Or, like an exaggerated Knight move,
the Wizard can jump three squares horizontally or vertically and then
one square to either side. The Wizard is bound to the color of its
starting square. The Wizard can jump over pieces to also control up
to twelve squares.(See diagram). The Wizard
is also classified as a leaper. It can move one square
diagonally in all four directions. Or, like an exaggerated Knight move,
the Wizard can jump three squares horizontally or vertically and then
one square to either side. The Wizard is bound to the color of its
starting square. The Wizard can jump over pieces to also control up
to twelve squares.(See diagram).
From the opening position, the Wizard can
immediately enter a game by jumping to squares: a2, j2 -- j7, a7.
|
|
|
How Pawns Move in Omega Chess
The Pawn can only move forward. From its initial position,
a Pawn in Omega Chess can move one, two or three squares forward
and after that, only one square at a time. A Pawn cannot move one square
initially and then two squares afterward. When making an initial double
or triple move a Pawn cannot jump over other pieces. While Pawns move
directly forward, they can only capture an opposing piece by moving one
square forward diagonally.
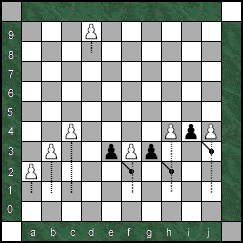 Pawn Promotion: The diagram shows a Pawn reaching the other side of
the board. When a Pawn reaches the far side of the board (the
10th rank) it is immediately promoted to any piece except a King (generally
to a Queen).
Pawn Promotion: The diagram shows a Pawn reaching the other side of
the board. When a Pawn reaches the far side of the board (the
10th rank) it is immediately promoted to any piece except a King (generally
to a Queen).
En Passant: The
principle for capturing an opposing Pawn en passant in Omega Chess
remains the same as in Standard Chess.
If a Pawn moves two or three squares initially and passes an opposing
Pawn on the fourth or fifth rank, the Pawn may be captured en passant.
The opposing Pawn moves onto the square through which the Pawn moved. Note
that in the diagram the Black Pawns which are capturing
en passant are on White's fourth and fifth rank, not on the third.
Capturing en passant is optional unless it is the only legal move
available. The capture must be made on the next move.
|